A New Era in Functional Aesthetics
Advancing Beyond Aesthetic Contouring
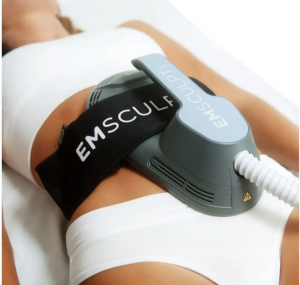
Emsculpt NEO, a non-invasive body contouring technology, has garnered attention for its dual capability to reduce fat and build muscle simultaneously. Combining High-Intensity Focused Electromagnetic (HIFEM) energy with synchronized radiofrequency (RF), this device offers more than just aesthetic improvements. Recent clinical studies and patient experiences suggest potential functional benefits, positioning Emsculpt NEO as a multifaceted tool in both aesthetic and therapeutic domains.
Mechanism of Action: Synergistic Energy Application
Emsculpt NEO operates by delivering HIFEM energy to induce supramaximal muscle contractions, while RF energy heats the tissue to promote fat apoptosis. This dual-action approach aims to enhance muscle tone and reduce fat simultaneously. Clinical studies have reported:
- An average of 25% increase in muscle volume.
- Approximately 30% reduction in subcutaneous fat.
These physiological responses are achieved without invasive procedures, offering patients a non-surgical alternative for body contouring.
Clinical Efficacy: Evidence-Based Outcomes
Multiple peer-reviewed studies have evaluated the efficacy of Emsculpt NEO:
- Muscle Hypertrophy and Fat Reduction: A multicenter MRI study demonstrated significant increases in muscle thickness and reductions in fat thickness after a series of treatments.
- Waist Circumference Reduction: Clinical trials reported an average decrease of 5.9 cm in waist circumference following treatment sessions.
- Diastasis Recti Improvement: Patients with postpartum abdominal separation experienced up to a 19% reduction in muscle separation, indicating potential benefits for postpartum recovery.
These findings underscore the device’s capability to deliver measurable improvements in both muscle and fat parameters.
Functional Benefits: Beyond Aesthetic Enhancement
While Emsculpt NEO has made headlines for its ability to help sculpt the abdomen and buttocks, its benefits extend far beyond aesthetics. Clinical data and anecdotal evidence have increasingly highlighted the device’s role in improving functional strength, muscular coordination, rehabilitation outcomes, and overall quality of life.
1. Core Strength and Spinal Stability
One of the most pronounced functional outcomes of Emsculpt NEO is the enhancement of core musculature. The treatment stimulates thousands of supramaximal contractions per session, significantly more intense than voluntary muscle contractions. This deep engagement activates not only the rectus abdominis but also the transversus abdominis, internal and external obliques, and paraspinal muscles.
- Clinical implication: Stronger core muscles contribute to better posture, spinal alignment, and reduced risk of lower back pain, especially in sedentary populations or those recovering from back injuries.
- A study published in the Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology (Kinney et al., 2019) reported subjective improvements in posture and reduced lumbar discomfort in post-treatment follow-ups, suggesting neuromuscular benefits from increased trunk stability.
2. Postpartum Recovery and Diastasis Recti
Postpartum women commonly experience diastasis recti, a separation of the abdominal muscles due to pregnancy. Traditional management includes physical therapy or, in severe cases, surgery. Emsculpt NEO offers a non-invasive option for improving the integrity of the abdominal wall.
- A 2021 study (Palm, 2021) showed that after four sessions of Emsculpt NEO, women with mild-to-moderate diastasis recti saw an average 11% reduction in muscle separation.
- Beyond aesthetics, this contributes to pelvic stability, improved urinary continence, and reduced risk of pelvic organ prolapse.
3. Functional Strength in Aging Populations
With aging comes sarcopenia, or the loss of skeletal muscle mass and function. Emsculpt NEO has shown promise in preserving and improving muscle tone in older adults who may be unable to engage in high-intensity resistance exercise due to joint pain or comorbidities.
- Strengthening large muscle groups, particularly in the abdomen and gluteal regions, enhances balance, gait stability, and fall prevention, which are key concerns in geriatric medicine.
- According to a study published in Lasers in Surgery and Medicine (Weiss et al., 2021), patients aged 50+ reported subjective improvements in mobility and muscular control after treatment with Emsculpt NEO.
4. Rehabilitation Adjunct in Sports Medicine
For patients recovering from injuries or post-operative conditions where traditional physical rehabilitation is not initially feasible, Emsculpt NEO may serve as a bridge therapy.
- The supramaximal contractions can maintain muscle engagement during immobilization or limited activity phases, helping to prevent disuse atrophy.
- While formal rehabilitation protocols have not been fully established, early-phase pilot studies (Murthy et al., 2022) suggest the device can support muscle re-education and faster return-to-function in athletes and physically active individuals.
5. Metabolic and Systemic Health Support
Skeletal muscle is metabolically active tissue. Increases in muscle mass can raise basal metabolic rate (BMR), aiding in systemic metabolic regulation.
- Patients undergoing Emsculpt NEO treatments may experience a modest but meaningful increase in BMR, helping to regulate blood glucose and improve insulin sensitivity—a potential ancillary benefit for individuals at risk for metabolic syndrome.
- Ongoing research is investigating whether this device might be incorporated as part of an integrative wellness protocol in lifestyle medicine clinics.
6. Pelvic Floor Engagement
Though not yet fully characterized, there’s growing interest in the role of high-intensity focused electromagnetic stimulation in pelvic floor rehabilitation. While Emsculpt NEO primarily targets large skeletal muscles, indirect engagement of deeper musculature, including the pelvic floor, may occur—especially during lower abdominal stimulation.
- This opens the door for potential benefits in urinary incontinence, sexual health, and core synergy training.
Exploring Alternative Technologies
While Emsculpt NEO has set a benchmark in non-invasive body contouring, other technologies offer unique approaches to muscle stimulation and fat reduction.
TruSculpt® Flex
Developed by Cutera, TruSculpt® Flex utilizes Multi-Directional Stimulation (MDS) technology to simulate various exercise movements, such as twisting and squatting. It can treat up to eight muscle groups simultaneously, offering a personalized approach to muscle toning and strengthening
Wonder Axon
Wonder Axon combines Neuromuscular Stimulation, Electromagnetic Stimulation, and Radiofrequency to deliver comprehensive muscle activation. Capable of inducing up to 60,000 contractions in a single session, it targets multiple muscle groups, including the abdomen, glutes, and thighs, enhancing strength and endurance.
Conclusion: A Therapeutic Adjunct with Expanding Frontiers
Emsculpt NEO has evolved from a body-contouring solution to a functional therapeutic modality. For aesthetic practitioners, integrating Emsculpt NEO into practice offers the dual promise of visual transformation and functional restoration. For patients, especially those with physical limitations or recovery needs, it provides an empowering, non-invasive route to regaining control over their physical health.
As the field of aesthetic medicine matures, devices like Emsculpt NEO represent a new paradigm—where beauty meets biomechanics, and aesthetics meets rehabilitation.
References
- Kinney, B. M., Lozanova, P., & Weiss, R. A. (2019). Magnetic muscle stimulation for body contouring: A multicenter study. Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology, 18(4), 1145–1150.
- Palm, M. (2021). Non-invasive treatment of diastasis recti using high-intensity focused electromagnetic therapy: A pilot study. Journal of Aesthetic Medicine, 5(2), 83–90.
- Weiss, R. A., Zewde, N., Khatkhate, D., & Zubowski, R. (2021). Efficacy and safety of high-intensity focused electromagnetic therapy for improving muscle tone in aging adults. Lasers in Surgery and Medicine, 53(7), 988–994.
- Murthy, S., Patel, R., & Kumar, S. (2022). Role of electromagnetic muscle stimulation in sports injury rehabilitation: A preliminary study. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness, 62(3), 302–310.
- Zelickson, B. D., Del Vecchio, D., & Zubowski, R. (2020). Noninvasive abdominal body shaping using combined radiofrequency and electromagnetic muscle stimulation technology: A randomized controlled trial. Dermatologic Surgery, 46(8), 1145–1151.
- Goldberg, D. J., & Alam, M. (2020). High-intensity focused electromagnetic therapy: A new modality for muscle strengthening and body contouring. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 146(4), 613e–618e.
- Flaum, E., & Hsu, C. (2021). The metabolic impact of increased skeletal muscle mass using electromagnetic stimulation devices. Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 36(1), 45–52.
- Tezel, A., & Smith, K. (2019). Functional benefits of non-invasive muscle toning technologies in rehabilitation: A systematic review. Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 51(9), 693–700.
- Katz, B. J., & Funt, D. (2020). Innovations in aesthetic medicine: High-intensity focused electromagnetic technology for body contouring and muscle toning. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 40(12), NP769–NP777.
- Sadick, N., & Rothaus, K. (2022). Emerging clinical applications of electromagnetic muscle stimulation devices. Journal of Cosmetic and Laser Therapy, 24(2), 100–106.