🔬 What is NAD⁺ and Why Does It Matter?
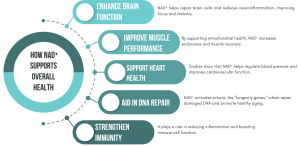
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD⁺) is a vital coenzyme found in all living cells. It plays a central role in energy metabolism by facilitating electron transfer during key cellular processes like glycolysis, the TCA cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. Without NAD⁺, cells would not be able to produce ATP—the main energy currency of the body.
But NAD⁺ is not just about energy. It’s also essential for DNA repair, circadian rhythm regulation, immune response, and cellular stress management. Enzymes like sirtuins and PARPs, which regulate gene expression and DNA repair respectively, are entirely dependent on NAD⁺ as a cofactor.
Why is NAD⁺ So Important?
NAD⁺ levels decline as we age, and this decline is associated with a wide range of cellular dysfunctions. Research shows that NAD⁺ depletion is a common feature in various age-related conditions, including metabolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, neurodegeneration, and reduced immune response.
This age-related decline affects mitochondrial function, genomic stability, and the body’s ability to handle oxidative stress. As such, maintaining or restoring NAD⁺ levels has become a key target in the science of aging and regenerative medicine.
The Link Between NAD⁺ and Aging

One of the leading theories of aging revolves around mitochondrial decline and oxidative damage. As NAD⁺ drops, the activity of sirtuins (NAD⁺-dependent enzymes that promote DNA stability and mitochondrial function) also declines. This contributes to cellular aging, reduced resilience, and a higher susceptibility to disease.
Animal studies have demonstrated that restoring NAD⁺ levels can extend lifespan, enhance mitochondrial function, improve cognitive performance, and reduce inflammation. In humans, while the long-term effects are still being studied, short-term trials suggest promising metabolic and physiological benefits.
Supplementation: Can You Really Boost NAD⁺ Levels?
To support or replenish NAD⁺ levels, several precursors are currently used in supplementation, including nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), nicotinamide riboside (NR), and niacin. These compounds have been shown to elevate NAD⁺ levels in both animal and human studies.For example, a 2018 clinical study found that daily NR supplementation significantly increased NAD⁺ levels in healthy middle-aged adults without serious adverse effects. Another study showed that NMN supplementation improved insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women, indicating potential metabolic benefits.
However, these interventions are still under investigation. Long-term safety, optimal dosage, and efficacy across diverse populations are areas that require further research.
NAD⁺ and Skin Health
While most studies focus on systemic health, emerging evidence suggests that NAD⁺ also plays a role in skin integrity and aging. Its role in DNA repair, oxidative stress reduction, and cellular regeneration points toward potential applications in dermatology and skin rejuvenation.
Sirtuins, which rely on NAD⁺, are also involved in collagen production and inflammatory regulation—key factors in maintaining youthful skin. However, more human data is needed to establish NAD⁺ supplementation as a mainstream approach in aesthetic medicine.
Who Should Consider NAD⁺ Support?
NAD⁺ precursors are often marketed to individuals seeking to maintain energy levels, cognitive clarity, metabolic health, and general resilience against aging. Preliminary studies suggest benefits in middle-aged to older adults, athletes, and individuals experiencing fatigue or metabolic imbalance.
That said, supplementation is not for everyone. Anyone considering NAD⁺ support should consult a medical professional to evaluate personal health needs, existing conditions, and possible contraindications.
Is NAD⁺ the Key to Feeling Young Again?
NAD⁺ is undoubtedly one of the most intriguing molecules in aging science. It plays essential roles in cellular maintenance, metabolic regulation, and repair. But while it holds promise, it’s not a miracle solution on its own.As research continues, it is becoming clear that the path to healthy aging involves multiple factors not just one molecule or therapy. A more holistic perspective is essential.
A Holistic View of Regenerative Wellness
NAD⁺ optimization is just one part of a broader regenerative wellness strategy that also includes balanced nutrition, quality sleep, physical activity, stress management, and other cellular-supportive therapies like cryotherapy, floatation therapy, and infrared therapy.
All of these elements work synergistically to support the body’s natural ability to repair and regenerate. Some of these services are available at Aura, which takes a holistic approach to wellness and longevity.
References
- Bogan KL, Brenner C. (2008). “Nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside: a molecular evaluation of NAD⁺ precursor vitamins in human nutrition.” Annu Rev Nutr, 28:115–30.
- Verdin E. (2015). “NAD⁺ in aging, metabolism, and neurodegeneration.” Science, 350(6265):1208–1213.
- Gomes AP et al. (2013). “Declining NAD⁺ induces a pseudohypoxic state disrupting nuclear-mitochondrial communication during aging.” Cell, 155(7):1624–1638.
- Canto C, Menzies KJ, Auwerx J. (2015). “NAD⁺ metabolism and the control of energy homeostasis: a balancing act between mitochondria and the nucleus.” Cell Metabolism, 22(1):31–53.
- Rajman L, Chwalek K, Sinclair DA. (2018). “Therapeutic potential of NAD⁺-boosting molecules: the in vivo evidence.” Cell Metabolism, 27(3):529–547.
- Imai S, Guarente L. (2016). “It takes two to tango: NAD⁺ and sirtuins in aging/longevity control.” NPJ Aging Mech Dis, 2:16017.
- Mills KF et al. (2016). “Long-term administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide mitigates age-associated physiological decline in mice.” Cell Metabolism, 24(6):795–806.
- Trammell SAJ et al. (2016). “Nicotinamide riboside opposes type 2 diabetes and neuropathy in mice.” Sci Rep, 6:26933.
- Yoshino J et al. (2018). “NAD⁺ intermediates: the biology and therapeutic potential of NMN and NR.” Cell Metabolism, 27(3):513–528.
- Martens CR et al. (2018). “Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD⁺ in healthy middle-aged and older adults.” Nat Commun, 9:1286.
- Yoshino M et al. (2021). “Nicotinamide mononucleotide increases muscle insulin sensitivity in prediabetic women.” Science, 372(6547):1224–1229.
- Gensler HL, Bernstein H. (1981). “Nicotinamide and skin cancer prevention.” Photochem Photobiol, 34(6):687–690.
- Revollo JR et al. (2004). “The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide riboside kinase is conserved in mammals.” J Biol Chem, 279(49):50754–50763.