Have you ever noticed that as the years go by, it becomes harder to stay in shape? Maybe you used to eat whatever you wanted without gaining weight, but now, even small indulgences seem to stick. Many people believe that weight gain is a natural part of aging, but the truth is more complicated.
Aging itself isn’t the main reason we gain weight. The real culprits are muscle loss, a slower metabolism, and lifestyle changes. The good news? Once we understand why this happens, we can take steps to prevent it!
The Role of Muscle in Weight Management
One of the biggest factors behind age-related weight gain is muscle loss, also known as sarcopenia. Sarcopenia is the natural decline in muscle mass that starts as early as our 30s. Studies show that adults lose 3-8% of their muscle mass every decade, and after age 60, the rate increases even more.
Why Does Muscle Matter?
Muscle is metabolically active, meaning it burns calories even when you’re resting. The more muscle you have, the more calories you burn throughout the day. When you lose muscle, your metabolism slows down, making it easier to gain fat even if your diet doesn’t change.
Imagine this:
- In your 20s, you might burn 2,000 calories a day.
- By your 50s, if you’ve lost muscle, your body might only burn 1,600 calories a day.
- If you keep eating the same amount, those extra 400 calories get stored as fat!
What Causes Muscle Loss?
- Lack of Strength Training
- If you’re not using your muscles, your body lets them shrink.
- Lower Protein Intake
- Older adults often eat less protein, which is essential for muscle repair.
- Hormonal Changes
- Testosterone and growth hormone levels decline with age, slowing down muscle growth.
How Lifestyle Changes Lead to Weight Gain
As we age, our lifestyles also change. Think about your daily routine compared to when you were younger:
- In our 20s and 30s, we tend to be more active—walking more, playing sports, or hitting the gym.
- As we get older, work, family, and other responsibilities take up more time, leaving less room for exercise.
- We may sit at desks for long hours, drive more, and generally move less.
This drop in activity makes it easier to gain weight because our bodies are burning fewer calories than before.
The “Middle-Age Spread”
Many people notice that as they get older, fat seems to accumulate in certain areas—especially the belly. This is due to hormonal changes and insulin resistance, making the body more likely to store fat around the midsection.
How to Prevent Age-Related Weight Gain
1. Prioritize Strength Training
One of the most effective ways to fight muscle loss is strength training. Lifting weights or doing resistance exercises twice a week can help you maintain or even build muscle.
If weightlifting sounds intimidating, don’t worry! You can start with:
- Bodyweight exercises (squats, push-ups, lunges)
- Resistance bands (gentle on joints, great for beginners)
- Yoga or Pilates (help with muscle tone and flexibility)
Studies show that adults who engage in regular strength training can increase muscle mass and boost metabolism—helping them maintain a leaner body.
2. Get Enough Protein
Protein is the building block of muscle, so eating enough is essential! Experts recommend at least 1.0–1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight for older adults. (Healthline, 2022)
Best sources of protein:
✅ Lean meats (chicken, turkey, fish)
✅ Eggs and dairy
✅ Beans and lentils
✅ Nuts and seeds
3. Stay Active Throughout the Day
Even if you can’t make it to the gym, you can increase movement in your daily routine:
- Take the stairs instead of the elevator.
- Walk or cycle for short trips instead of driving.
- Stretch or do light exercises while watching TV.
Every bit of movement helps keep your metabolism higher!
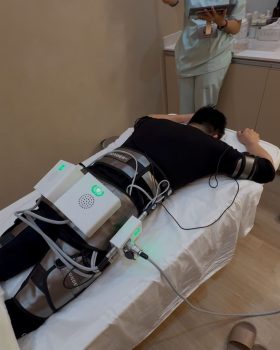
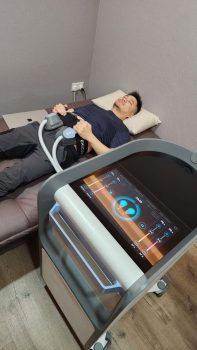
4. Consider Advanced Muscle Stimulation Technology
For those struggling to maintain muscle mass, modern technology offers powerful solutions. Emsculpt Neo and Wonder Axon are two cutting-edge treatments designed to build muscle and reduce fat simultaneously using advanced energy-based technologies.
Emsculpt Neo utilizes high-intensity focused electromagnetic (HIFEM) technology combined with radiofrequency (RF) to stimulate muscle growth while simultaneously burning fat. Wonder Axon, on the other hand, employs a hybrid bioelectric stimulation technique that enhances deep muscle contractions, improving tone and strength.
I had the opportunity to personally try both treatments, and the experience was nothing short of impressive. The intense muscle contractions felt like an extreme workout session—without the exhaustion or joint strain that comes with traditional exercise. Over a few sessions, I noticed significant improvements in muscle definition and strength, especially in areas that are difficult to target with conventional training.
Science backs these benefits as well. A study by Dr. Diane Duncan demonstrated that Emsculpt treatments led to improved muscle mass and functional mobility in older adults. Participants not only gained strength but also experienced better walking ability and reduced risk of falls—key factors in maintaining independence as we age.
For those looking to combat muscle loss and maintain strength without spending hours in the gym, Emsculpt Neo and Wonder Axon offer a game-changing alternative. Whether used alone or alongside exercise, these technologies provide an effective way to stay strong, lean, and active well into later years.
Final Thoughts: It’s About Muscle, Not Just Age
Gaining weight as we get older isn’t inevitable—it happens because of muscle loss, a slowing metabolism, and less movement.
The solution? Stay active, build muscle, eat enough protein, and take advantage of modern advancements in muscle stimulation technology.
Aging doesn’t have to mean weight gain. The best time to start is now!
References
- Harvard Health Publishing. (2023). Preserve your muscle mass. Retrieved from health.harvard.edu
- Cleveland Clinic. (2023). Sarcopenia (Muscle Loss): Symptoms & Causes. Retrieved from my.clevelandclinic.org
- Adams, V. (2018). Electromyostimulation to fight atrophy and to build muscle: facts and numbers. Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia, and Muscle, 9(4), 631–634. Retrieved from pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- Healthline. (2022). How to Fight Sarcopenia (Muscle Loss Due to Aging). Retrieved from healthline.com
- Kinney, B., & Loos, M. S. (2020). Noninvasive Induction of Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy and Hyperplasia: Effects of High-Intensity Focused Electromagnetic Field. Aesthetic Surgery Journal, 40(5), 568–574. Retrieved from academic.oup.com
- Medical News Today. (2022). Sarcopenia: Causes, Symptoms, and Management. Retrieved from medicalnewstoday.com
- Duncan, D. I., & Dinehart, S. M. (2021). High-Intensity Focused Electromagnetic Technology in Elderly Patients: Improved Functional Movement and Muscle Strength. Aesthetic Surgery Journal Open Forum, 3(1), ojab013.